An Indefinite While Loop That Displays Hello as Long as the User Wants to Continue in Python
Overview
Python While Loop is a programming construct used to repeatedly execute a set of statements until a condition is met. When the condition in the programme becomes false, the line immediately after the loop is performed. While loop is classified as an indefinite iteration.
Scope
- In this article, we will see what are while loops in Python.
- Then we will move forward to look syntax of the while loop.
- Then, we will move forward to know the use cases of while loops and examples.
What is While Loop in Python?
While loop statement in python is used to repeatedly execute statement(s). The number of times the while loop is executed is not known in advance, so the while loop is called an Indefinite Iteration statement. It will keep on repeatedly executing as long as a while condition is true, and it will stop repeating only if the condition becomes false.
Let us say you are asked to print your name in python 100 times. The most naive approach would be to type/copy-paste the statement print("Name") 100 times and execute. But that is such a redundant task with 100 lines of python code.
The best possible approach will be if you make use of the while loop statement in python. And here's how it works: Write a while loop, place the print("Name") inside the while loop, write a condition in such a way that it fails after executing 100 times, and voila.
This code is at most 4-5 statements, unlike the naive approach, which took 100 statements. So, in other words, while loop makes our life easy.
Syntax of While Loop in Python
while expression: statement(s)
Below is an explanation of the components in syntax:
- statement(s) can be a single statement or a block of statements that are uniformly indented. Python treats uniformly indented statements as a block.
- expression is a statement in the condition statement in python, it is evaluated to be True or False. Python interprets all non-zero values as true and 0 or None as false. While loop keeps on repeating as long as the expression returns True. It will stop when the expression returns False
- while is the keyword that is used to write a while loop statement.
- the while expression is the head/starting of the while loop statement, while the statement(s) that are uniformly indented make up the body(inside) of the while loop.
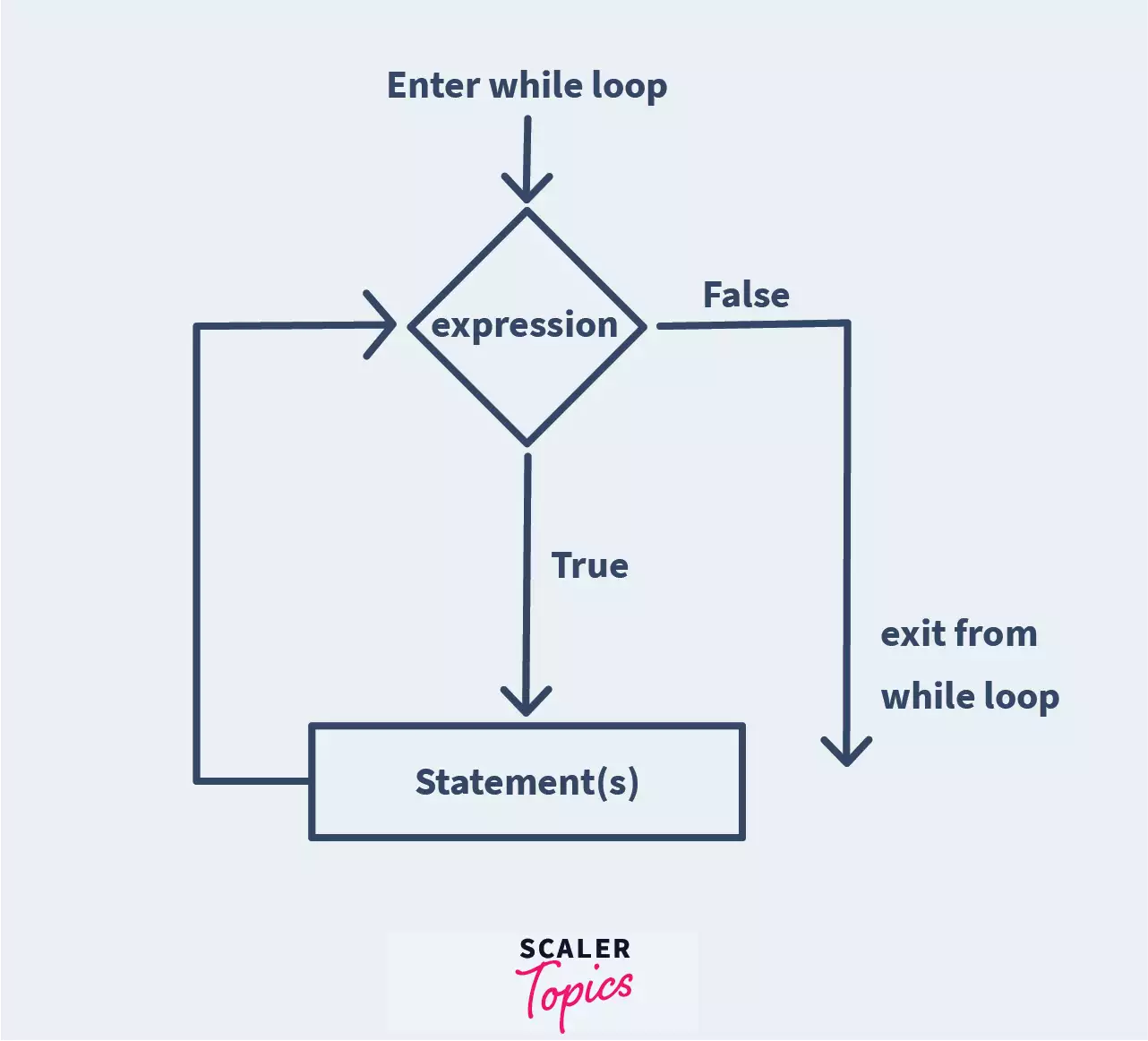
Working of while:
- First, the expression is evaluated. If it returns true, control is passed to the indented statement(s) inside the while loop.
- All the statements that are indented to the right below the while loop for the body of the while loop and are executed.
- Once the statements are executed, control is again passed to the expression, and the expression is evaluated again. If it returns true, the body is executed again. This repeats until the expression returns false.
- Once the while loop break, control passed to the next unindented line of the while loop
We shall explore the working of while loop more clearly with an example in the next sections of the article.
FlowChart of While Loop in Python
Example of Python While Loop
#1 Write a program to print a name ten times in python using the while loop
Program:
count = 0 ; while count < 10 : print ( "My name is Vidyut" ) count += 1
Output:
My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut
Explanation:
- The objective is to print the "My name is Vidyut" string 10 times.
- We took a variable count and initialized it to 0
- The expression 'count < 10' is evaluated, and since 0 < 10, control goes inside the while loop
- The 'print' statement and count += 1 statement, which is uniformly indented from the body of the while loop. They are both executed. The string is printed to output once, and the count value gets incremented by 1.
- Now, control goes back to the expression 'count < 10'. And since 1 < 10, control again goes inside the while loop.
- This process is repeated till the count value is incremented to 10, and the print statement has been executed a total of 10 times.
- Now, since the condition 10 < 10 returns false, the loop breaks, the body of the while loop is not executed, and the control jumps to the next statement after the while statement.
While Loop with else
While statement in python also supports else statement in association with it. The else statement is optional. Below points illustrate the working of while else:
- The else statement written after the while statement will be executed when the expression of while returns False.
- So, else statement will be executed once the execution of the while is completed normally( By expression returning False).
- If a break statement is executed inside the while loop and the execution is stopped, then else block is skipped, and control jumps directly to the statement below the while..else.
- Notice the difference between the statements inside the else block and the statements written below the while..else.
- The statements inside the else block will be skipped if the while loop breaks abruptly. In the normal case of while expression returning false, the else will be executed.
- The statements below the while..else block will be executed in both the cases when the while expression returns false and also when the while breaks abruptly(using break).
Syntax:
while expression: statement(s) else : Statement(s)
The body of else can be a single statement or a block of uniformly indented statements. The else is executed only once after the while loop condition returns false and the loop breaks.
Example:
count = 0 ; while count < 10 : print ( "My name is Vidyut" ) count += 1 else : print ("String is printed ten times!")
Output:
My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut My name is Vidyut String is printed 10 times!
Explanation:
- The objective is to print the "My name is Vidyut" string ten times.
- We took a variable count and initialized it to 0
- The expression 'count < 10' is evaluated, and since 0 < 10, control goes inside the while loop
- The 'print' statement and count += 1 statement, which is uniformly indented form the body of the while loop. They are both executed. The string is printed to output once, and the count value gets incremented by 1.
- Now, control goes back to the expression 'count < 10'. And since 1 < 10, control again goes inside the while loop.
- This process is repeated till the count value is incremented to 10, and the print statement has been executed a total of 10 times.
- Now, since the condition 10 < 10 returns false, the loop breaks, and the body of the while loop is not executed, and control jumps to the next statement after the while statement, which is the else statement.
- Now, the body of else statements gets executed, and the print statement is executed.
- Then, the flow of control goes to the next statement after the while-else statement.
Single Statement While Loop in Python
If there is only one statement in the body of the while loop, the statement can be placed in the same line as the while header statement. This variant is supported in python. The below syntax makes this clear.
while expression: statement
This is only allowed for a single statement if there are multiple statements, all of them should be written inside the body of the while loop, and that too uniformly indented.
Example:
count = 0 while count < 10 : print ( "I run Infinitely" )
Output:
The String "I run Infinitely" getting printed on the console in infinity
Explanation:
- The count is initialized to 0
- The expression count < 10 is evaluated, and the single statement inside the while loop body is executed.
- The control then jumps back to the expression count < 10, and it again returns true.
- This process keeps on running infinitely, as the expression count < 10 will never return false since we are not modifying the count value anywhere.
- So this loop can also be called an Infinite while loop. Let us clearly define and understand what an infinite while loop is in the next section.
The Infinite While Loop in Python
The Infinite while loop is a loop that never stops its repeated execution because the expression ( condition ) defined in the while header will never return False. The example we saw in the above section is one such infinite while loop.
There can be many use cases of Infinite while loop in programming. A simple instance is a system/program that keeps on running without stopping, like a server program. So that the client program can connect to the server program anytime as long as the server program keeps running.
Let us look at an example Infinite while loop program
count = 0 while count != 1 : name = str ( input ( "What is your name? " )) print ( "Hi " + name)
Output:
What is your name? Rahil Hi Rahil What is your name? Raavi Hi Raavi What is your name? Rejesh Hi Rejesh What is your name? Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py" , line 3 , in <module> name = str ( input ( "What is your name? " )) KeyboardInterrupt
Explanation:
- Here, the expression count != 1 is always True. So the body of the while loop is executed on infinite.
- This loop keeps on asking for input and keeps on outputting the value, till we hit CTRL + C, which generates a keyboard interrupt to break the loop.
While Loop Control Statements in Python
Loop control statements/ keywords in python written inside a while loop affect the flow of execution of the while loop. They alter the normal execution of a loop. Below are the loop control statements that are supported in python:
Continue Statement:
Continue statement written inside the body of while loop returns the flow of control back to the expression in the header, skipping the execution of the rest of the statements inside the body.
Example:
count = 0 while count < 10 : count += 1 ; if (count == 5 ): continue print ( "The value of the count is " + str (count))
Output:
The value of count is 1 The value of the count is 2 The value of the count is 3 The value of the count is 4 The value of the count is 6 The value of the count is 7 The value of the count is 8 The value of the count is 9 The value of the count is 10
Explanation:
- Count is initialized to 0
- count < 10 is evaluated, and the body of the while is executed.
- When the value of count is equal to 5. The if statement condition count == 5 will be true. And the statement inside if which is continue is executed.
- Once the continue statement gets executed, control jumps directly to the while header again, skipping all the statements below it hence the print statement "The value of count…" is not executed in case of count == 5
- After the count becomes six again, the flow of control is similar to the normal while loop.
Break Statement:
Break statement inside the body of a while loop will stop the repeated execution and bring the control out of the while loop. It is like an abrupt force stop of a while loop. If it is a while..else statement, then the else part is also skipped when a break statement is executed. Control jumps directly to the statement below the while..else statements.
Example:
count = 0 while count < 10 : count += 1 ; if (count == 5 ): break print ( "The value of the count is " + str (count))
Output:
The value of count is 1 The value of the count is 2 The value of the count is 3 The value of the count is 4
Explanation:
- Count is initialized to 0
- count < 10 is evaluated, and the body of the while is executed.
- When the value of count is equal to 5. The if statement condition count == 5 will be true. And the statement inside if the break is executed.
- Once the break statement gets executed, control jumps directly out of the while loop, skipping all the statements below it, and the repeated execution of the loop stops. Hence no values equal to and below five got printed as output.
Pass Statement:
A pass statement can be seen as a dummy/empty statement. It is used to write empty loops, empty blocks, empty functions, classes, etc. It doesn't really affect the flow of control. It is used to keep the flow seamless.
Example:
count = 0 while count < 10 : count += 1 ; if (count == 5 ): pass print ( "The value of the count is " + str (count))
Output:
The value of count is 1 The value of the count is 2 The value of the count is 3 The value of the count is 4 The value of the count is 5 The value of the count is 6 The value of the count is 7 The value of the count is 8 The value of the count is 9 The value of the count is 10
Explanation:
- Count is initialized to 0
- count < 10 is evaluated, and the body of the while is executed.
- When the value of count is equal to 5. The if statement condition count == 5 will be true. And the statement inside if which is pass is executed.
- In this example, when a pass gets executed, since it is a dummy statement, the flow is not disturbed, and the if condition gets evaluated without any errors and control and goes to the next statement after the if, which is the print statement.
Conclusion
We have reached the end of the article. The examples we took in this article are very basic to give you a clear, in-depth understanding of the while loop in python. Once you get the hang of while loop and its variants, you can try to explore the below classic while loop programs in python.
- Sum all the integers in a given list of python
- Factorial of a number using while loop in python
- Generate Fibonacci sequence using while loop in python
- Print the Multiplication table for a given number using the while loop in python
- Check if the given number is prime or not using the while loop in python
Source: https://www.scaler.com/topics/python/while-loop-in-python/
0 Response to "An Indefinite While Loop That Displays Hello as Long as the User Wants to Continue in Python"
Post a Comment